Spring MVC Exception Handling
In this tutorial we take a look at how to use Spring MVC Exception Handling. We can design our application to deal with exceptions in various ways. We could handle the exceptions in the methods where they occur, but most of the time this leads to cluttered and duplicated exception handling code, so we are not showing you this. The following is an overview of what we’ll see in this article:
- Handling controller local exceptions – We can catch the exceptions using a @ExceptionHandler locally in the controller. This will override any pre-defined global exception handler.
- Global exception handler – Catch exceptions globally across all controllers.
- Custom 404 response – Instead of the default 404 page, we return a JSON response containing a detailed message.
- Custom error pages – Instead of showing the default error pages of your servlet container, we create a custom error page displaying the occurred error message.
- Business Exceptions – by annotating custom business methods with @ResponseStatus spring automatically returns the status code defined in the annotation.
Spring MVC Exception Handling
To start, we are using the following Java Object to return a fault code together with a detailed message. As this class will be used across all examples, we show you this first. Later on we look at the previous examples into more detail.
package com.memorynotfound.model;
public class Error {
private int code;
private String message;
public Error() {
}
public Error(int code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}Handling Controller Local Exceptions
Using Spring MVC we can handle the exceptions occurred in a controller locally. We have two options, either by annotating a method with the @ExceptionHandler annotation and provide the class of the exception that needs to be handled. Or, we can also implement the HandlerExceptionResolver where we need to implement the resolveException(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, Object handler, Exception ex), this method will resolve any exceptions occurred inside the controller methods.
Controller Local Exceptions with @ExceptionHandler
Here is an example how to handle exceptions locally in the controller they occurred. We annotate a method using the @ExceptionHandler annotation and provide the exception (or an array of exceptions) the method needs to handle. The more specific exception takes priority over the general one.
package com.memorynotfound.controller;
import com.memorynotfound.model.Error;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/courses")
public class CourseController {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<Object> get(){
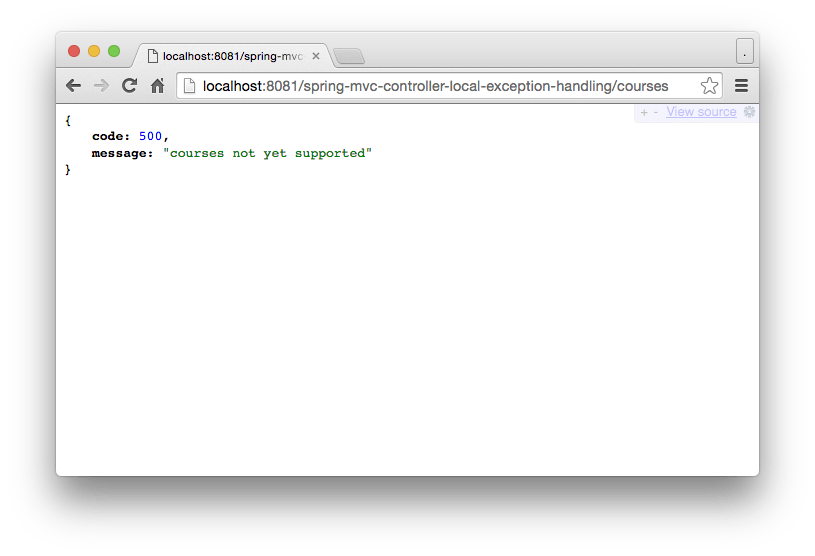
throw new RuntimeException("courses not yet supported");
}
@ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Error> handle(RuntimeException ex){
System.out.println("controller local exception handling @ExceptionHandler");
Error error = new Error(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), ex.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<Error>(error, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}The return type can be a String, which is interpreted as a view name, a ModelAndView object, a ResponseEntity, or you can also add the @ResponseBody to have the method return value converted with message converters and written to the response stream.
URL: http://localhost:8081/spring-mvc-controller-local-exception-handling/courses
Controller local Exceptions with HandlerExceptionResolver
Here is an example implementing the HandlerExceptionResolver. By implementing this interface we must override the resolveException() method. This method will handle all exceptions thrown by the controller. In order to get the type of the exception, we need to do an instanceof operation.
package com.memorynotfound.controller;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.json.MappingJackson2JsonView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/students")
public class StudentController implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<Object> get(){
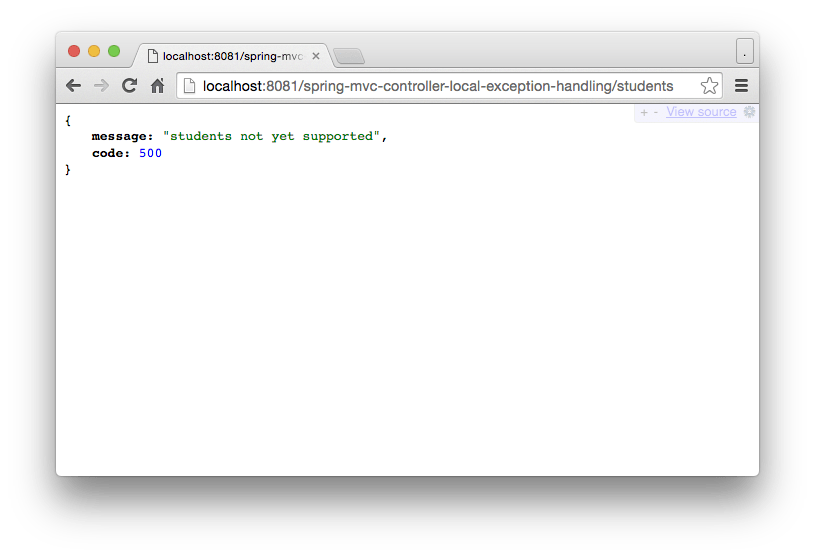
throw new RuntimeException("students not yet supported");
}
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, Object handler, Exception ex) {
System.out.println("controller local exception handling HandlerExceptionResolver");
resp.reset();
resp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
resp.setContentType("text/json");
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView(new MappingJackson2JsonView());
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException){
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
model.addObject("code", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value());
model.addObject("message", ex.getMessage());
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
model.addObject("code", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value());
model.addObject("message", ex.getMessage());
}
return model;
}
}In this example we return a JSON response by setting the view of the ModelAndView to an instance of the MappingJackson2JsonView class. We also add a status code to the response via the HttpServletResponse#setStatus() in order to tell the client some error has occurred.
URL: http://localhost:8081/spring-mvc-controller-local-exception-handling/students
Global Exceptions Handler
The following example shows how to handle exceptions globally, across all controllers. This really encapsulates the DRY-principle. Because our exception handling code is located only in a single place.
package com.memorynotfound.controller;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/courses")
public class CourseController {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<Object> getList(){
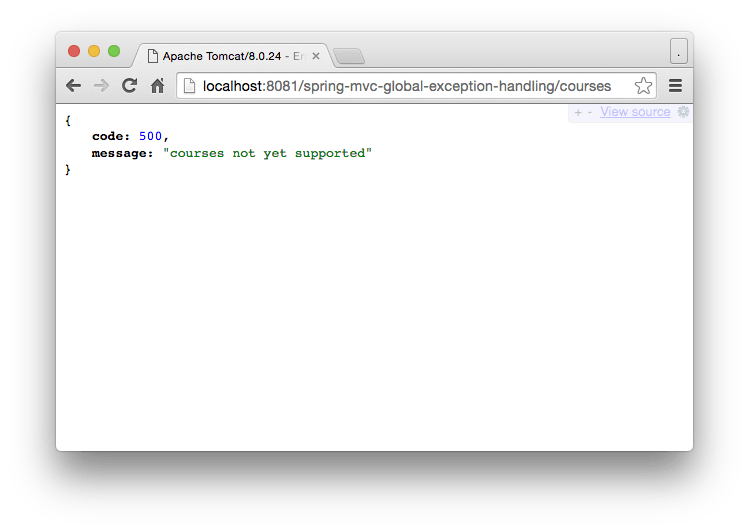
throw new RuntimeException("courses not yet supported");
}
}The @ExceptionHandler method becomes a global exception handler when we move this method in a separate class annotated with the @ControllerAdvice annotation. The ResponseEntityExceptionHandler is not mandatory but by using ResponseEntityExceptionHandler you can override the standard Spring MVC exceptions.
package com.memorynotfound.exception;
import com.memorynotfound.model.Error;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Error> handle(RuntimeException ex){
Error error = new Error(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), ex.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<Error>(error, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}URL: http://localhost:8081/spring-mvc-global-exception-handling/courses
Custom 404 Response
By default, when a page/resource does not exist the servlet container will throw a 404 page. When you are developing API’s and you want a custom 404 JSON response, here is how.
package com.memorynotfound.config;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class ServletInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { WebConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected DispatcherServlet createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext servletAppContext) {
final DispatcherServlet servlet = (DispatcherServlet) super.createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
servlet.setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(true);
return servlet;
}
}We need to tell the DispatcherServlet to throw the exception if no handler is found. We can do this by setting the throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound servlet initialization parameter to true. The previous code will set the property to true when you are configuring your servlet container using java configuration.
When using XML to configure the servlet container, you can set the property using the following code.
<servlet>
<servlet-name>rest-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>Next, we catch the NoHandlerFoundException and return a custom error message containing an error code and detailed description.
package com.memorynotfound.exception;
import com.memorynotfound.model.Error;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.NoHandlerFoundException;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(NoHandlerFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Error> handle(NoHandlerFoundException ex){
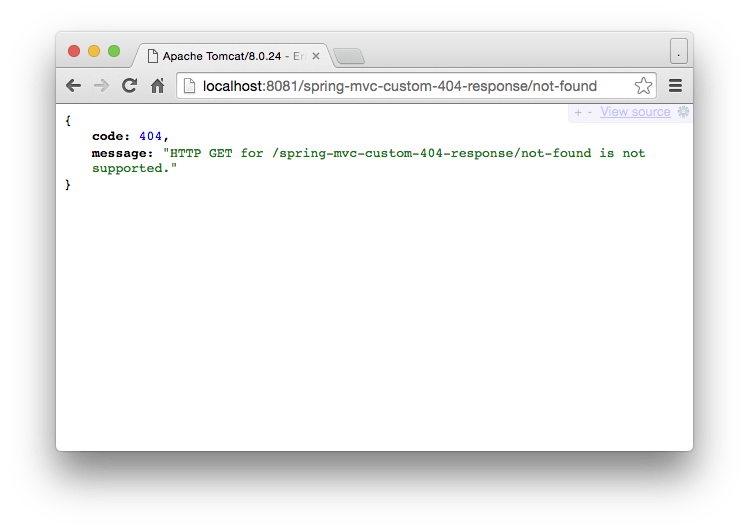
String message = "HTTP " + ex.getHttpMethod() + " for " + ex.getRequestURL() + " is not supported.";
Error error = new Error(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value(), message);
return new ResponseEntity<Error>(error, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}URL: http://localhost:8081/spring-mvc-custom-404-response/not-found
Custom Error Pages
The following example shows how you can create custom error pages. Take a look at the CourseController, there are two controller methods registered. The first will throw a RuntimeException, the second will throw a ArithmeticException. We define a controller-local exception handler using the @ExceptionHandler annotation and return a ModelAndView containing the occurred exception and forward it to the error page.
package com.memorynotfound.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/courses")
public class CourseController {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getList(){
throw new RuntimeException("courses not yet supported");
}
@RequestMapping(value = "{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String get(@PathVariable int id){
throw new ArithmeticException("cannot divide by zero");
}
@ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class)
public ModelAndView handle(RuntimeException ex){
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("error");
model.addObject("exception", ex);
return model;
}
}This is an example how to configure the SimpleMappingExceptionResolver using Java configuration. This resolver enables you to take the class name of any exception that might be thrown and map it to a view name.
@Bean
public SimpleMappingExceptionResolver exceptionResolver(){
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver resolver = new SimpleMappingExceptionResolver();
Properties exceptions = new Properties();
exceptions.put(ArithmeticException.class, "error");
resolver.setExceptionMappings(exceptions);
return resolver;
}This is an example how to configure the SimpleMappingExceptionResolver using XML configuration
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver">
<property name="exceptionMappings">
<props>
<prop key="java.lang.ArithmeticException">error</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>The error.jsp page displays the occurred exception.
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Spring MVC Exception Handling</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Spring MVC Exception Handling</h1>
${exception.message}
</body>
</html>URL: http://localhost:8081/spring-mvc-custom-error-pages/courses
When we access the controller method, the page is forwarded to the error page displaying the occurred exception.
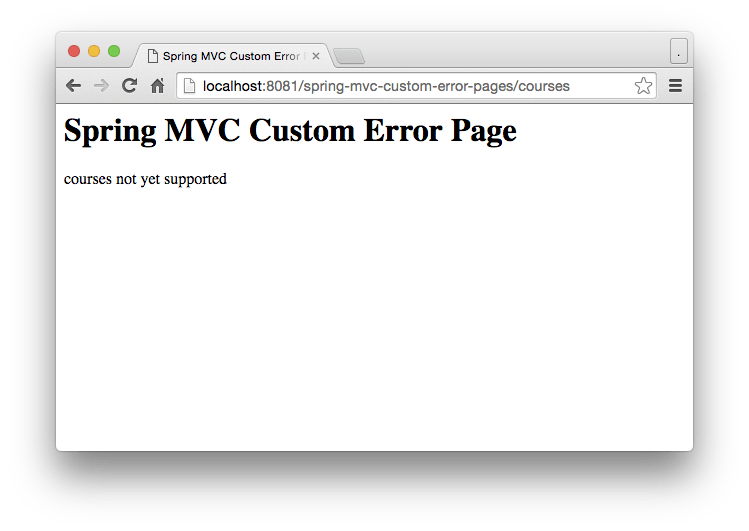
Custom Exceptions annotated with @ResponseStatus
You can annotate an exception with the @ResponseStatus. Here you can provide a status code and a detailed exception message. When the exception is raised, the ResponseStatusExceptionResolver handles it by setting the status of the response accordingly.
package com.memorynotfound.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, reason = "Course not found")
public class CourseNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
public CourseNotFoundException() {
}
}You can just throw the exception inside the controller and the ResponseStatusExceptionResolver will handle it automatically.
package com.memorynotfound.controller;
import com.memorynotfound.exception.CourseNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/courses")
public class CourseController {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<Object> getList(){
throw new CourseNotFoundException();
}
}URL: http://localhost:8081/spring-mvc-response-status/courses
When we access the controller, the following page is displayed.
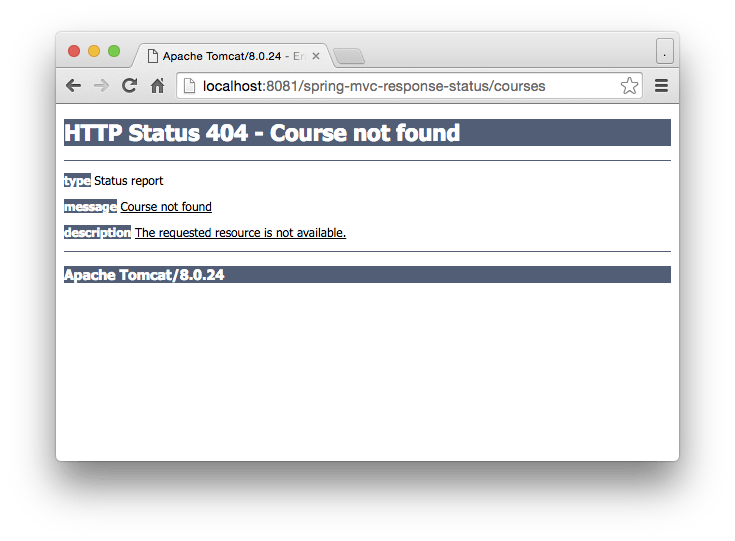
Download
From:一号门

COMMENTS